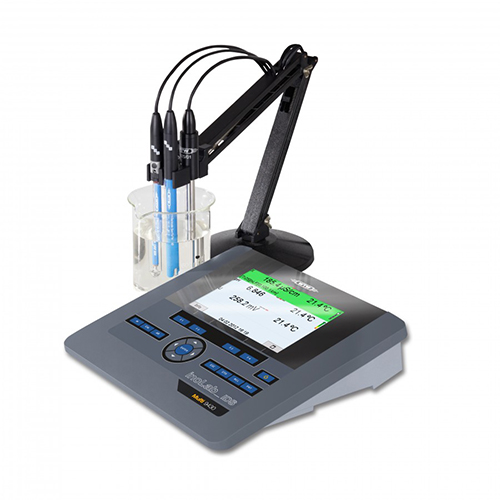
pH Meters
The pH value of foods has a direct effect on the growth of microorganisms and therefore on food quality and safety. For this reason, many companies use the pH value as a quality characteristic for evaluating their food. For example, the pH value is of great importance in the manufacture of meat, sausage, delicatessen and dairy products. The pH value is an important quality parameter in the food sector. It particularly affects the properties of meat and meat-based products, especially with regard to water binding capacity, taste, colour, tenderness and shelf life. In the bakery sector, the acidity of the sourdough can be determined by means of the pH value. In the case of products such as salad dressings, the pH value helps to ensure consistent quality or consistent acidity of the product.